Do you hope to find 'c3 photosynthesis'? Here you can find questions and answers on the topic.
C3 carbon fixationC₃ atomic number 6 fixation is the most common of three metabolic pathways for carbon regression in photosynthesis, on with C₄ and CAM. This cognitive operation converts carbon dioxide and ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP, a 5-carbon sugar) into 2 molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate through the foll… Plants which usance only the Melvin Calvin cyclefor fixing the carbon dioxide from the air ar known as C3 plants. In the first step of the cycle CO2reacts with RuBPto green groceries two 3-carbon molecules of 3-phosphoglyceric venomous (3-3-Phosphoglyceric acid3-Phosphoglyceric blistering is the compound acid of glycerate 3-phosphate. The glycerate is a biochemically significant metabolic average in both glycolysis and the Melvin Calvin cycle. This anion is often termed as PGA when referring to the Calvin cycle. Stylish the Calvin wheel, 3-phosphoglycer…).
Table of contents
- C3 photosynthesis in 2021
- C3 photosynthesis vs c4
- C3 photosynthesis temperature
- Advantage of c3 photosynthesis
- C3 photosynthesis advantages
- What is the c3 pathway in photosynthesis
- C3, c4 and cam plants
- C3 plants
C3 photosynthesis in 2021
.PNG) This picture demonstrates c3 photosynthesis.
This picture demonstrates c3 photosynthesis.
C3 photosynthesis vs c4
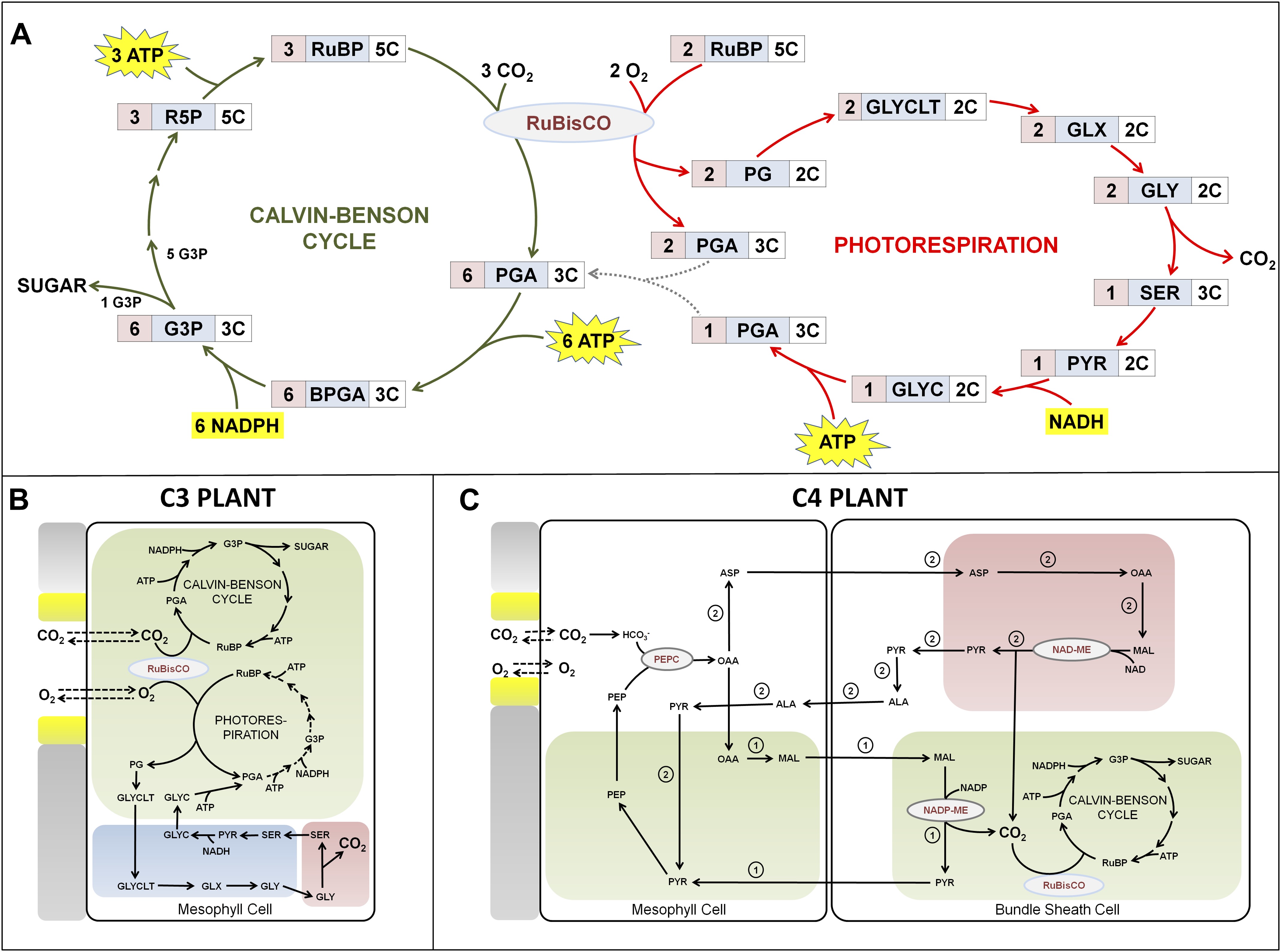 This image demonstrates C3 photosynthesis vs c4.
This image demonstrates C3 photosynthesis vs c4.
C3 photosynthesis temperature
 This image illustrates C3 photosynthesis temperature.
This image illustrates C3 photosynthesis temperature.
Advantage of c3 photosynthesis
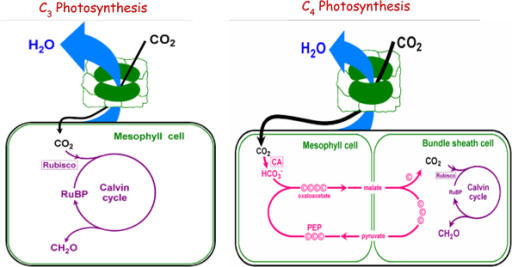 This picture representes Advantage of c3 photosynthesis.
This picture representes Advantage of c3 photosynthesis.
C3 photosynthesis advantages
 This image demonstrates C3 photosynthesis advantages.
This image demonstrates C3 photosynthesis advantages.
What is the c3 pathway in photosynthesis
 This image representes What is the c3 pathway in photosynthesis.
This image representes What is the c3 pathway in photosynthesis.
C3, c4 and cam plants
 This image illustrates C3, c4 and cam plants.
This image illustrates C3, c4 and cam plants.
C3 plants
 This image demonstrates C3 plants.
This image demonstrates C3 plants.
Which is the ancestral path of C3 photosynthesis?
C3 photosynthesis is the ancestral path- In C4 plants, the C3 cycle of the photosynthetic pathway way for carbon fixation and occurs in all taxonomic plant is restricted to interior cells within the leaf (usually the groups. The term C3 photosynthesis is based on the obser- bundle sheath cells).
Which is an example of a C3 plant?
The C3 plants, originating during Mesozoic and Paleozoic eras, predate the C4 plants and still represent approximately 95% of Earth's plant biomass. C3 plants lose 97% of the water taken up through their roots to transpiration. Examples include rice and barley.
What does C3 and C4 mean in photosynthesis?
C3 and C4 photosynthesis The majority of plants and crop plants are C3 plants, referring to the fact that the first carbon compound produced during photosynthesis contains three carbon atoms. Under high temperature and light, however, oxygen has a high affinity for the photosynthetic enzyme Rubisco.
Where does C3 carbon fixation take place in plants?
This reaction occurs in all plants as the first step of the Calvin–Benson cycle. In C4 plants, carbon dioxide is drawn out of malate and into this reaction rather than directly from the air. Cross section of a C3 plant, specifically of an Arabidopsis thaliana leaf.
Last Update: Oct 2021